Shopify stores live or die by two things: how quickly they serve customers and how clearly search engines understand their pages. This blueprint concentrates on the technical levers that reliably move organic traffic—page speed, structured data, and crawlability—while showing a practical automation path using Trafficontent to scale content that supports product pages. ⏱️ 10-min read
If you run a Shopify store, an agency, or manage SEO for multiple merchants, this is a hands-on guide. Expect reproducible metrics, small weekly wins, and a deployable checklist you can plug into your release workflow. I’ll show what to measure, how to fix the usual bottlenecks, and how to automate content and monitoring so your SEO improvements stick.
Shopify speed foundations
Start with a reproducible measurement baseline: run Lighthouse or PageSpeed Insights across a representative set of product and collection pages using mobile throttling and several device types. Track three metrics consistently—Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), and Total Blocking Time (TBT)—and log results in a shared dashboard. Set clear targets: aim for mobile LCP under 2.5 seconds, CLS below 0.1, and TBT under 300ms as starting benchmarks. These give you objective goals and make regressions obvious.
Don’t try to fix everything at once. After any major change, choose one metric to improve that week: shave 0.2s off LCP, cut CLS by 0.02, or reduce TBT by 50ms. Small, verifiable wins build momentum. Common bottlenecks on Shopify are oversized images, render-blocking CSS, and heavy third-party scripts; prioritize fixes that reduce payload and shorten the critical rendering path. Quick wins include enabling image optimization (WebP/AVIF where supported), deferring noncritical scripts, minifying CSS/JS, and tightening font loading with font-display: swap and font subsetting. Log each change with before/after screenshots and Lighthouse runs so the team can see the impact.
Theme and code optimization for Shopify 2.0
Shopify 2.0 changed theme architecture—JSON templates and modular sections make it easier to render lean pages if you design for that. Start by breaking pages into small, reusable blocks and mapping data through JSON templates rather than duplicating markup. Prefer render over include in Liquid templates: render isolates block scope, preventing variable leakage and repeated rendering that bloats output.
Inline only the CSS necessary above the fold and push everything else later. Use async or defer attributes on noncritical scripts and move nonessential JS to the footer. Consolidate assets into a single CSS bundle and as compact a JS bundle as practical to reduce HTTP requests on product pages. Remove unused CSS and JavaScript during theme builds—pruning unused blocks and assets paid for during development often remains neglected.
Use Shopify’s Theme Check and Theme Inspector during development and integrate them into CI so regressions are caught before a deploy. Keep a performance budget—maximum CSS and JS bytes for product and collection pages—and fail builds that exceed it. A lean theme structure reduces cognitive overhead and yields faster pages that are simpler to maintain.
App footprint and script governance
Third-party apps commonly introduce the slowest dependencies. Audit your app footprint: list active apps, note what each injects (scripts, iframes, CSS), and measure the cumulative cost. If an app delivers nonessential widgets, consider lazy loading them or removing them entirely. Where possible, replace heavy apps with lightweight storefront code or server-side integrations that don’t add client execution time.
Adopt script governance: load third-party scripts asynchronously, wrap them in timeouts, or gate them behind user interaction. For example, defer reviews widgets until the review tab is opened, or load chat widgets after the first interaction. Use network and CPU throttling in Lighthouse to capture realistic impacts and prioritize the scripts that hurt LCP and raise TBT. When you must keep a script, host minimal portions locally or use a smaller vendor implementation to reduce latency and avoid multiple DNS lookups.
Finally, track app changes in a lightweight changelog and include a simple rollback plan when updating or adding apps. This prevents surprise performance regressions during sales spikes or seasonal campaigns.
Image and media optimization
Images are the single largest payload on many Shopify product pages. Serve responsive images with srcset and sizes so browsers download the appropriate width for the device. Generate multiple widths (for example: 400, 800, 1200 px) and let the browser select the best fit. Prefer WebP or AVIF for supported browsers and fall back to JPEG/PNG where necessary; Shopify’s image CDN can deliver formats dynamically, but precompressing before upload still helps.
Implement loading="lazy" for noncritical images and use low-fi placeholders or skeletons for above-the-fold areas that aren’t visible immediately. This reduces perceived load time and minimizes layout shifts. For hero images, resize to the display dimensions—1200px wide is often sufficient for full-width desktop heroes—rather than uploading monstrous originals.
Video governance matters too. Host large videos offsite (YouTube/Vimeo) and embed using a click-to-load preview or a lightweight poster frame; avoid autoplay. If you must host product videos, provide short, optimized previews and compress aggressively. Use captions and transcripts for accessibility and SEO. Do a quick verification after changes: check image waterfall in Chrome DevTools, confirm WebP/AVIF delivery via network headers, and rerun Lighthouse to ensure LCP improves.
Structured data implementation for product pages
Structured data is a high-leverage, low-cost way to improve visibility and click-throughs. Implement a single JSON-LD block in your product template that contains Product, Offer, and BreadcrumbList markup. The product object should include name, image, description, SKU, brand, and an offers object with price, currency, availability, and priceValidUntil when applicable. If you collect reviews, add aggregateRating and review entries to improve eligibility for rich results.
Automate JSON-LD generation by mapping the script to authoritative data sources—Shopify product fields, metafields, or your ERP—so prices and availability stay accurate as variants change. Inaccurate structured data is worse than none; it can trigger manual actions or cause misleading rich snippets. Validate changes with Google’s Rich Results Test and schedule a check after any price change, sale, or template update.
Don’t forget BreadcrumbList schema: it’s lightweight and clarifies site structure to search engines. Where questions commonly arise on a product page (shipping, returns), consider an FAQ schema block, but only for genuine content visible to users. Keep JSON-LD compact, and place it in the product.liquid/section template so every product inherits the same logic. Track schema errors in a weekly audit and fix them before large promotional pushes.
Crawlability and indexation
Shopify provides a default robots.txt and sitemap.xml—use them as your starting point. Open /robots.txt and /sitemap.xml and confirm critical product, collection, and blog pages are not blocked. If you add apps, custom routes, or proxy endpoints, re-audit robots rules. Block only truly low-value pages (internal search results, admin endpoints) and test changes in a staging environment first.
Canonical tags keep signals consolidated. Shopify generally outputs canonical URLs, but confirm that paginated or filtered collection pages point to the primary version rather than parameterized or filtered variants. Use canonical tags conservatively—don’t canonicalize different product variants unless they are near-duplicates. For moved content, implement 301 redirects and validate them in the redirects section of Shopify or via your CDN.
Watch duplicate content created by filters and tags. Where those pages provide no unique value, apply noindex or canonicalize to the core collection page. Ensure rel=prev/next is present on paginated lists so crawlers understand sequence and don’t index every page as separate content. Finally, keep sitemaps updated: exclude noindexed pages and ensure new product URLs are added as part of your product onboarding process to speed indexation.
URL structure and internal linking
Clean URLs help both users and crawlers. Keep slugs short, descriptive, and keyword-relevant: /products/organic-arabica-coffee or /collections/kitchen-appliances. Use lowercase and hyphens; avoid long query strings for primary navigational pages. Consistent naming reduces the need for redirects later and builds trust across ads, social, and email links.
Design internal linking like a prioritized map. Each category should link to its most important products; product descriptions and guides should include contextual links to related SKUs with descriptive anchor text (avoid “click here”). Implement visible breadcrumbs and mark them up with BreadcrumbList schema—this assists navigation and strengthens semantic signals.
Minimize crawl depth by surfacing priority product pages within two or three clicks from the homepage. Reserve faceted navigation for users, not crawlers—avoid exposing a vast combinatorial space of filter URLs to search engines. Use canonical tags for filtered views, and where relevant, add noindex to paginated or filtered shells that produce thin content. A tidy URL and linking strategy reduces wasted crawl budget and focuses authority on pages that convert.
Automation and monitoring for Shopify SEO (Trafficontent workflow)
Automation turns one-off optimizations into sustained performance. Create a weekly cadence: run automated Lighthouse tests, validate structured data with the Rich Results Test, and review GSC for index coverage or spikes in 404s. Route alerts for thresholds (LCP > 2.5s, CLS > 0.1, sudden 404 increases) to Slack or email with a simple runbook for the on-call engineer.
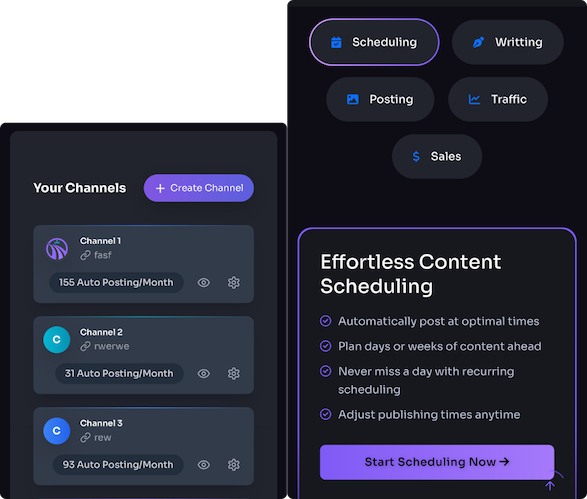
Trafficontent fits neatly into this automation strategy. Use Trafficontent to auto-generate and schedule SEO-friendly blog posts that link to priority product pages—this strengthens internal linking and creates relevant landing pages for long-tail keywords. A practical workflow: define target keywords and products in Trafficontent, generate optimized post drafts (titles, meta, headings, and suggested internal links), review and enrich the content, then schedule auto-publishing to Shopify. Each post should include contextual links to product pages with UTM parameters for tracking and should be mapped to an editorial calendar that coincides with product launches or promotions.
Trafficontent can also automate routine checks: schedule weekly audits for structured data drift and surface mismatches between product metafields and JSON-LD. Integrate its publishing API with your analytics to tag and track organic KPIs—impressions, click-throughs, and conversions—for content pieces that point to product pages. This closes the loop between creation and measurable SEO impact.
Pre-deployment checklist and release workflow
Preventing regressions is as important as fixing problems. Before any theme or app deployment, run a preship checklist that includes: Lighthouse runs on a staging URL, Theme Check and Theme Inspector reports, structured data validation, robots.txt and sitemap review, and a comparison of asset sizes (CSS/JS). Require signoff on each item from an owner and include clear acceptance criteria (e.g., LCP on staging must be within 10% of production baseline).
- Automated tests: Lighthouse scores, TBT/LCP/CLS thresholds, and structured data checks.
- Manual checks: confirm canonical tags, rel=prev/next on paginated collections, and robots/sitemap exposures.
- Rollback plan: snapshot the previous theme, export critical assets, and note app configurations to restore quickly.
- Post-deploy verification: run the same Lighthouse and schema tests on production and log results into the dashboard.
Embed these steps into your CI/CD pipeline so human error is reduced. Maintain a lightweight changelog that lists theme version, files changed, tests run, owners, and acceptance results. That changelog becomes a searchable history when troubleshooting later, and it dramatically reduces time to revert if a release introduces a performance regression.
Real examples & quick mini-cases
Concrete outcomes help prioritize work. Example A: a mid-size store with slow product pages traced the problem to oversized hero images and missing lazy loading. They resized hero images to a 1200px target, implemented srcset, enabled lazy loading for below-the-fold assets, and relied on Shopify’s image CDN. They added a lightweight JSON-LD block via a small theme snippet to expose product name, price, availability, and review rating. Four weeks later, LCP dropped from 3.8s to 2.6s and on-page conversions rose about 7%—a classic speed→conversion win.
Example B: a catalog-heavy merchant struggled with slow indexation and duplicate filter URLs. The team audited robots.txt and sitemap.xml, implemented canonical tags on filtered and paginated pages, and updated sitemap generation to exclude thin, duplicate views. They added JSON-LD for breadcrumb and product data and validated everything with the Rich Results Test. New product pages began indexing within 24 hours instead of several days; index coverage improved by roughly 15–20% and the number of 404s on launches dropped noticeably because canonical and redirect practices were consistent.
Across both cases the lessons are consistent: start with speed, make structured data accurate and automated, and remove crawl obstacles. Small, measured changes compound into meaningful traffic and conversion improvements.
Next step: pick one product page, run a Lighthouse audit, and apply this blueprint end-to-end. Use Trafficontent to create a targeted blog post that links to that product, schedule it for publication, and observe the impact on internal linking, indexation speed, and organic metrics over the next month.