If you run a WordPress store—WooCommerce or a custom shop—publishing SEO-driven blog content can feel like juggling marketing, content-calendar-align-blog-posts-with-product-launches-and-promotions/" rel="nofollow noopener noreferrer">product launches, and developer priorities. This guide lays out a practical, automation-ready framework for building reusable blog post templates that streamline keyword research, drafting, and publishing while keeping product pages and conversions front and center. ⏱️ 9-min read
You’ll get an actionable roadmap: how to align content goals to product taxonomy, a template anatomy optimized for rich results, an AI-assisted keyword workflow with human checks, and a Trafficontent-powered calendar that automates publishing, social snippets, and email nudges. Each section gives concrete examples and rules your team can apply today.
Define Goals and SEO Signals for Ecommerce Blogs
Start by translating business objectives into content goals. Decide what success looks like in numbers: a 20% lift in organic visits to category pages, a 10% increase in blog-driven add-to-carts, or a target AOV lift from content-driven upsells. These metrics—traffic, rankings, CTR, conversions, revenue per post—become the north star for every template you build.
Next, identify the SEO signals that should influence content choices. Prioritize search intent alignment (informational vs. transactional), keyword difficulty, topical authority, CTR potential from SERP features, and backlink opportunity. For example, a “how to choose a gaming laptop” guide targets high-intent informational queries that naturally link to product category pages; a “best gaming laptops under $1,000” post is more transactional and should include product cards and price-focused schema.
Map each content goal to your product taxonomy: tag blog posts with category slugs, assign them to product lines, and maintain a clear breadcrumb structure. Track KPIs monthly—organic traffic, rankings for target keywords, time on page, and conversions from blog referrals—and set a quarterly review cadence. Establish baseline quality thresholds for readability, factual accuracy, and engagement so you can measure improvement over time.
Core Template Architecture for WordPress Ecommerce Posts
A reliable template reduces decision fatigue and preserves SEO signals across hundreds of posts. Design a content block blueprint that guides the reader from first impression to purchase: hero image, hook intro, value bullets, product mention, content body, FAQ, and a clear CTA. Keep the hero image at a standard size (1200x628) with descriptive alt text; that helps social previews and accessibility.
- Header: site-wide navigation and the H1 that mirrors your title tag.
- Hero/Hook: benefit-first opening sentence and 3–5 value bullets that tell readers what they'll gain.
- Product embeds: inline product cards with price and availability snippets (generated from WooCommerce or Trafficontent hooks).
- Body sections: H2s like Overview, Benefits, How to Use, Comparison, and Alternatives to structure skimmable reading.
- FAQ: 3 concise Q&A items encoded as FAQPage schema for rich results.
- CTA block: Shop now, Explore category, or Compare products—include tracking parameters for attribution.
Include structured data: Article markup (headline, author, date, image), BreadcrumbList, and Product/FAQ snippets where relevant. Standardize metadata scaffolding so titles, descriptions, and social tags follow predictable patterns—this reduces manual errors and supports automation workflows in Trafficontent.
Keyword Research Strategy: AI-assisted and Human Validation
Start keyword research with seeds pulled from product SKUs, category names, customer questions, and store analytics. Examples: “blue running shoes,” “eco-friendly yoga mat,” and “how to choose a gaming laptop.” Feed these seeds into Trafficontent’s AI expansion to generate long-tail ideas and cluster terms by intent—informational, navigational, and transactional.
Trafficontent can produce topic clusters so you publish a coherent series rather than disconnected posts. For example, a “yoga” cluster might include “best yoga mats for hot yoga” (transactional), “how to clean a yoga mat” (informational), and “yoga mat materials explained” (awareness). Use AI to scale ideation, then validate each suggested keyword manually: check search volume, keyword difficulty, current SERP features, and whether the intent matches your business model.
Assign each keyword to a template type and funnel stage. High-consideration terms and comparisons belong on buyer guides with product embeds; quick transactional queries should be routed to category or product pages. Build a keyword-to-template mapping sheet that your writers and Trafficontent automation rules reference—this ensures consistent targeting and reduces cannibalization when multiple pages target related phrases.
On-Page SEO Template Elements
Turn on-page SEO into repeatable rules. Create title and meta description templates with placeholders for the primary keyword, category, and brand. Practical examples: “[Primary Keyword] – Essential Guide to [Category] | BrandName” for guides, and “Buy [Primary Keyword] for [Category] | Free Shipping over $50” for conversion-focused posts. Keep meta descriptions under 160 characters and include a clear value proposition.
Standardize header hierarchy: one H1 that mirrors the title tag, H2s for main sections, and H3s for subsections. Keep paragraphs short (2–4 sentences) and use descriptive headings—“Overview,” “Benefits,” “How to Choose,” and “FAQs.” For slugs, adopt a readable format like /category/primary-keyword/ or /category/primary-keyword-intent/, all lowercase with hyphens, and avoid overly long URLs.
Define internal linking rules in your template: every post should link to at least two category pages and one related product using natural anchor text. Create canonical URL practices to prevent duplicate content across category and blog pages—use canonical tags pointing to the primary product or category page when appropriate. Include image alt-text standards (describe the image and include a keyword when natural) and require at least one in-body image per 400 words to break text and support social sharing.
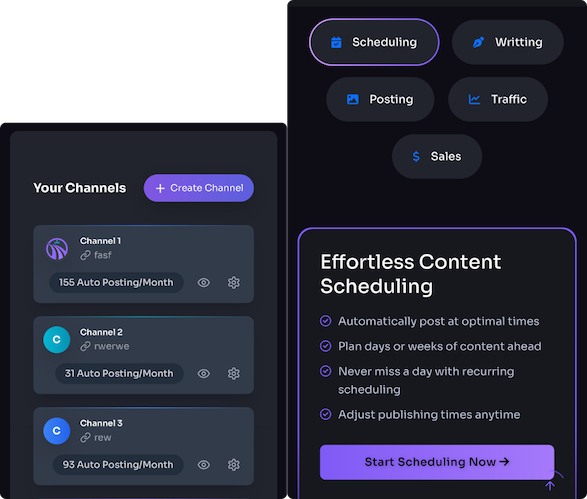
Content Calendar and Workflow with Automation (Trafficontent)
Turn planning into a system with Trafficontent. Begin each month by defining 2–3 content themes tied to product cycles and promotions (for example: “Back-to-School Tech,” “Sustainable Home Picks,” or “Holiday Gift Guides”). Map each planned article to a product line, persona, and funnel stage. For each item, create a starter brief—goal, target keyword, outline, CTA, and media needs—to plug into Trafficontent’s template engine.
Establish automation rules: set posts to draft automatically from a chosen template, generate 1–2 social snippets and image suggestions, and queue them for scheduled publishing. Use Trafficontent to auto-populate product cards from WooCommerce or Shopify feeds so prices and availability are always current. Define human checkpoints for QA: content review, fact-checking, and accessibility checks before the post goes live.
For cross-platform distribution, create flows that publish to WordPress, push social snippets to Buffer or native APIs, and trigger an email nurture in your ESP 48 hours after publish. For product updates, use conditional triggers: when a product price changes or a SKU is marked “new,” Trafficontent can generate an alert draft or auto-publish a product update post with the predefined “new product” template. This reduces manual work while keeping content timely and tightly connected to commerce events.
Template Variants for Ecommerce Scenarios
Not every post should use the same layout. Create specialized template variants for common ecommerce scenarios so each post drives the right action and SERP signal.
- New product launch: Hook with the problem it solves, list 3–5 standout features, include quick-spec bullets (weight, battery life, price range), and a “Buy now” product card. Add hands-on impressions to boost authenticity.
- Best-sellers roundup: Lead with social proof and link to category pages. Use sortable product cards by price or rating, and include review highlights or sales counts.
- Buyer guide & comparison: Structure decision criteria, comparison tables, and recommended picks for different budgets. Include callouts like “Best for beginners” or “Best value.”
- Tutorials and how-tos: Include step-by-step instructions, short videos or GIFs, and a materials or product list that links to relevant items.
- Case studies and announcements: Use a narrative intro, outcomes with metrics (e.g., “reduced setup time by 40%”), and a lesson section for readers.
Decide evergreen vs. time-bound behavior when you pick a template. Evergreen templates include update prompts every quarter; time-bound posts must include publication date prominence and clear archival or update rules so your editorial calendar can either refresh or retire content automatically.
SEO Plugins and Performance Best Practices
Your templates should be supported by a lean performance stack and the right plugins. Use Yoast SEO or Rank Math to manage metadata templates, schema injection, and canonical tags. Avoid running overlapping features across multiple SEO plugins to prevent conflicts—pick one and standardize settings across the site.
Performance matters for rankings and conversions. Implement caching (WP Rocket), image optimization (Smush or Imagify), and a CDN (Cloudflare or StackPath). Enable lazy loading for images and videos to improve Core Web Vitals. For images, serve WebP where possible and automate alt-text from template fields with human edits during QA.
Use your SEO plugin to generate BreadcrumbList, Article, Product, and FAQ schema, then verify with Google’s Rich Results Test. Enforce canonical URLs and ensure your sitemap includes blog posts and product pages. Finally, add accessibility checks into your template QA: descriptive alt text, 16px+ base font, high-contrast colors, and keyboard-friendly navigation for any interactive product cards or carousels.
Content Quality and Compliance Checklist
Quality isn’t optional—templates should bake in editorial and legal safeguards. Require a friendly, consistent tone that aligns with the brand but also mandates factual verification: link to vendor specs for product claims and add a short “Sources” section at the end. Run originality checks and keep an author byline with credentials to enhance E-E-A-T signals. Schedule quarterly refreshes for evergreen posts and immediate updates for posts tied to product changes.
Accessibility and user trust are essential. Templates should demand descriptive alt text, captions for videos, readable font sizes, and semantic HTML (headings and lists). For sponsored posts or affiliate links, include disclosures near the top and again before any CTA in a clear, conspicuous format to comply with FTC guidelines.
Legal: limit data capture to what’s necessary, reference your privacy policy when collecting emails via lead magnets, and maintain a simple process for removing or correcting product information if supplied by vendors. During QA, include checks for duplicate content and internal competition—ensure two pages aren’t trying to rank for the exact same keyword without canonical or consolidation rules.
Analytics and Iteration: Measuring SEO Impact
Measure impact by template as well as by post. Tag posts with a template identifier in your analytics (Trafficontent can auto-tag posts on publish). Track organic sessions, rankings for target keywords, CTR from search results, and conversion rate (add-to-cart or revenue) per template. For example, compare “buyer guide” templates against “best-sellers” templates to see which drives more conversions for mid-funnel shoppers.
Run quarterly template audits: review top- and bottom-performing posts, examine on-page metrics (bounce rate, time on page), and check SERP feature presence. Use these insights to refine keyword choices, adjust H2 structures, and test different CTA placements. A/B test meta descriptions and title variants for high-impression pages and iterate on product card designs to improve CTR and average order value.
Finally, close the loop with Trafficontent automation: when analytics show a drop in CTR or rankings for a keyword cluster, create a ticket to refresh content, add FAQ schema, or update product embeds. Make iteration part of the template lifecycle—templates should evolve based on data, not remain static.
Next step: pick one product category that underperforms in organic traffic, create a Trafficontent template mapped to its top three buyer intents, and schedule two posts this month—one evergreen guide and one product roundup—to test the framework end-to-end.