Great SEO programs aren’t built on sprints—they’re built on compounding wins. The fastest way to create those gains is to pair an AI-first planning workflow with platform-native automation on WordPress or Shopify. Done right, you’ll publish strategically, promote automatically, and spend your human time on the few decisions that actually move the needle. ⏱️ 8-min read
This guide shows content managers, growth marketers, and solo founders how to stand up an editorial calendar that aligns to business goals, clusters topics with AI and real search data, produces SEO-first briefs at scale, and uses automation to ship, distribute, and iterate—all on repeat.
Set clear business and SEO objectives for the calendar
Start with the market, not the machine. Identify core personas (for example: shopper, researcher, repeat buyer) and list their top questions and search intents. Use Google Search Console and on-site analytics to spot high-intent queries you’re not answering yet. For WordPress, emphasize lead-gen intent; for Shopify, prioritize product/category intent and revenue per visit.
Translate that insight into measurable SEO goals for the next 6–12 months. Examples include: increase organic sessions by 30% in six months, move 10 priority keywords into the top 3, lift CTR on key pages by 1–2 points, or raise MQLs/demos from organic by 40%. Track impressions, positions, CTR, backlinks, conversions, and revenue using GA4, Search Console, and a rank tracker.
Make the calendar accountable to the business. Tie each content type to an outcome—traffic growth, qualified leads, product sales, or retention—and prioritize topics by estimated ROI. Define cadence and ownership so execution is boringly reliable:
- Cadence: a practical baseline is one pillar and three cluster posts per month (per product line or solution area).
- Ownership: strategy (SEO lead), brief creation (content strategist), writing (in-house or freelancer), editing (editor/PM), publishing & QA (SEO specialist), promotion (social/email owner).
- Review rhythm: monthly performance review to reallocate effort toward the highest-impact clusters.
Build a priority topic model with AI plus real search data
AI can surface opportunities quickly, but only data will keep you honest. Use both.
Workflow overview:
- Seed: list product categories, features, and customer pains. Add competitor head terms and your internal site search queries.
- Expand with AI: prompt an AI model to generate topic clusters, questions, and intent labels (informational, comparison, transactional, post-purchase). Ask it to suggest pillar candidates and 8–12 supporting posts per pillar.
- Validate with data: check topics and keywords in Search Console (queries and pages), GA4 (landing pages, engagement), and research tools like Ahrefs/SEMRush (volume, difficulty, SERP features).
- Score and rank: build a lightweight scoring rubric that weights opportunity and fit.
Suggested scoring rubric:
- Search volume (normalized)
- Keyword difficulty/competitiveness
- Intent match to your funnel stage
- Business value (closeness to revenue or MQL)
- Existing authority (current rankings/backlinks)
Output a ranked list of pillar topics with mapped cluster posts for each funnel stage. Example: a Shopify store selling eco water bottles might choose “Reusable Water Bottles Guide” as the pillar, with clusters like “Stainless vs. Tritan: Which Lasts Longer?”, “How to Clean a Reusable Bottle,” and “Best Reusable Bottles for Hiking.” A WordPress SaaS blog might anchor a pillar on “Data Governance for SMBs,” supported by “Data Governance Checklist,” “Data Governance vs. Data Security,” and “How to Pitch Governance to Your CFO.”
Design pillar-cluster architecture and content types
Structure guides both readers and search engines. Build a clear pillar–cluster architecture and stick to it.
Pillar content: create a cornerstone page (typically 2,000+ words) that explains the big idea, answers core questions, weaves in data or product specifics, and links out to every related cluster. Include an evergreen table of contents and refresh it quarterly.
Cluster content: publish focused posts (800–1,200 words) that drill into subtopics—how-tos, tutorials, comparisons, case studies, FAQs. Optimize each for long-tail queries, and tailor tips to your platform (e.g., Shopify product filters or WordPress blocks).
Internal linking: use descriptive anchors and consistent rules so the structure is maintainable:
- Every cluster links to its pillar (2–5 links per cluster to related content).
- The pillar links back to clusters in context (don’t bury links in a wall of tags).
- Maintain clean canonicals on duplicate-prone formats (e.g., Shopify tag pages).
- Audit links quarterly; automation (e.g., SEO Workflow Automation or a Smart Scheduler) can flag or fill gaps.
Translate topics into the formats your CMS supports best—long-form guides, comparison tables, product-led tutorials, FAQs, and even short video scripts that live alongside posts. On WordPress or Shopify, standardize templates so every new piece lands with correct headings, schema, and CTAs.
Generate SEO-first article briefs and templates using AI
Briefs are where scale meets quality. Use AI to draft structured briefs that keep intent, SERP fit, and brand guardrails front and center, then add human judgment.
Each brief should include:
- Title options, H1–H3 outline, and suggested word counts
- Primary and secondary keyword clusters with search intent
- Meta title and meta description
- Recommended internal links and a clear CTA
- Schema suggestions (e.g., FAQPage, HowTo, Product)
- Source links and research notes
Embed on-page checks in your template: meta tags, schema.org snippets, image alt text, canonical tags, and heading best practices. Pre-fill internal link suggestions for WordPress or Shopify so writers don’t start from zero. Tools like Trafficontent Blog Automation or Surfer can provide on-page guidance and push drafts to your CMS.
Keep collaboration tight: share briefs as editable docs, assign roles, and route drafts through review via Slack, Asana, or Trafficontent automation. Add a human QA checklist to every brief:
- Accuracy and citations verified
- Brand voice and claims approved
- Keyword intent satisfied; no stuffing
- Internal links added; CTA aligned to funnel stage
- Plagiarism and factual checks complete
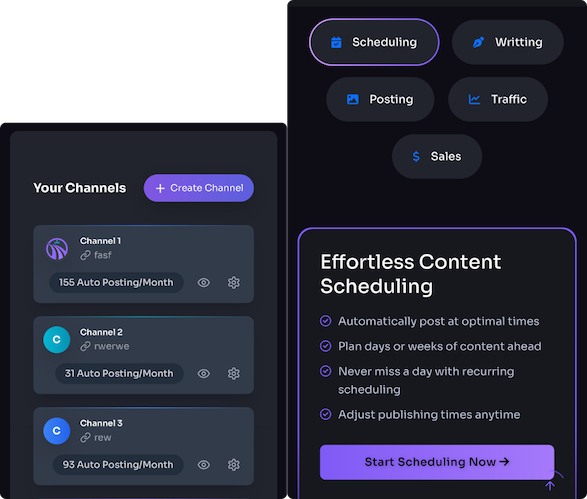
Build the editorial calendar and connect platform automations
Turn briefs into a reliable production line. Use a visual board (Trello, Asana) with columns for idea, drafting, editing, scheduled, and published so status is visible at a glance. Attach the brief, target keywords, and your SEO checklist to each card. If you use Trafficontent, connect SEO Workflow Automation so keyword and linking tasks stay in view.
Automate publishing schedules. Set recurring publish dates and time slots; let a Smart Scheduler pick optimal times and avoid conflicts. Connect the board to WordPress Blog Automation or Shopify Blog Automation so drafts, metadata, slugs, canonicals, and featured images sync automatically to the CMS—no copy-paste, fewer errors.
Track simple metrics on the card (pageviews, organic sessions, position deltas) and adjust cadence based on results. This closes the loop and makes improvements compounding instead of sporadic.
Automate distribution: social, newsletter, and short video
Don’t rely on “we’ll tweet it later.” Automate distribution so every post gets consistent exposure with minimal effort.
Social scheduling: use Buffer, Hootsuite, or Trafficontent’s Social Media Automation to generate platform-specific captions and schedule multiple variants per article. Add UTM parameters, test different angles (stat, benefit, contrarian take), and stagger posting across time zones on X, LinkedIn, and Facebook.
Email newsletter automation: trigger sends from your RSS or CMS via Mailchimp, ConvertKit, or Klaviyo (great for Shopify). Keep emails short and value-dense with a single clear CTA. Segment by interest so subscribers see the most relevant posts.
Short-video repurposing: pull a 30–60 second hook from each article—an insight, framework, or result. Edit in Descript, CapCut, or VEED, add subtitles, and schedule to TikTok, Reels, and Shorts. Pipeline ideas directly to creators from the calendar to keep momentum.
Measure referral growth monthly and double down on the channels consistently sending engaged traffic.
Measure, iterate, and run content experiments
Decide which KPIs matter—organic sessions, scroll depth, engagement rate, conversions—and check them weekly so you catch small signals early. Link GA4 and Search Console for a full view of queries, impressions, and landing-page performance; tag campaigns with UTMs so promotion impact is visible.
Run simple, repeatable experiments: test titles, meta descriptions, intros, and layout patterns. Use CMS A/B tools where available, or ship controlled variants and track with GA4. Change one thing at a time and run until you have statistically meaningful results.
Let data drive updates. Prioritize pages with high impressions but low CTR for title/meta rewrites; pages with traffic but weak engagement for content refreshes; top performers for repurposing into email and video. Feed winning topics back into AI to suggest expansions, FAQs, and related clusters that extend your footprint.
Real-world signal: a mid-size Shopify store running a pillar-cluster plan with Trafficontent’s Shopify Blog Automation plus Social Media Automation saw ~35% more organic sessions in five months and moved eight target keywords to page one. A B2B SaaS blog on WordPress used Blog Automation and Newsletter Automation to turn two long posts per week into email series and social snippets; organic traffic climbed ~50% in six months and inbound demo requests nearly doubled.
Governance, scaling, and cost control for AI workflows
Guardrails keep quality high as you scale volume.
Usage guidelines: define what AI can do (outlines, draft copy, meta, headings, link suggestions) and what humans own (facts, brand voice, legal claims, final edits). Require an editor checklist and automated plagiarism checks. If using Trafficontent’s WordPress or Shopify Blog Automation, codify which automations are allowed and when to flag for manual review.
Cost monitoring: track API spend and model choices using provider dashboards and platform reports. Set monthly budgets and alerts. Cache or reuse outputs for repeat tasks; use cheaper models for ideation and higher-quality models for final editing to keep bills predictable.
Scaling plan: standardize reusable templates, modular prompts, and an editorial SOP so new writers plug in quickly. Automate publication and distribution with SEO Workflow Automation and a Smart Scheduler, but scale editorial review capacity proportionally. Measure ROI in two dimensions: organic lift per topic cluster and time saved per post.
Next step: pick one product line or solution area, ship one pillar plus three clusters, connect your CMS and distribution automations, and schedule a 30-minute weekly review. The compounding starts when you publish with intent—and keep iterating on a tight loop.